Every modern computing device is a mix of physical parts and digital instructions. This mix is the heart of today’s technology.
This mix includes hardware and software working together. They work as a team to handle information and tasks.
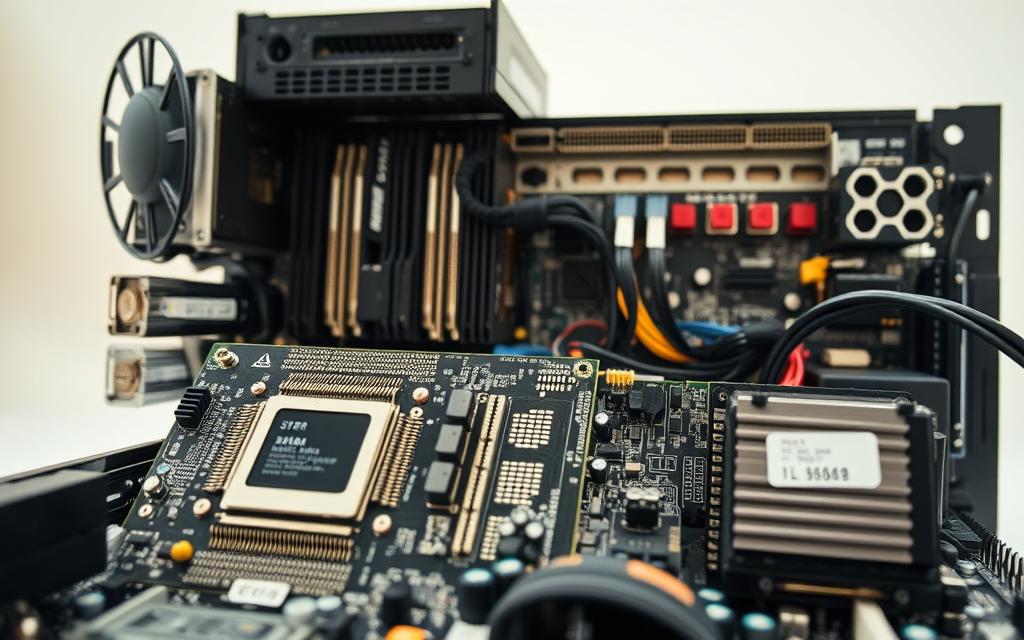
All computers have basic parts, no matter their design or use. The motherboard is like the brain, linking everything together.
The central processing unit does the math, and memory is for temporary work. Storage keeps data safe for a long time, and the power supply gives it the energy it needs.
An operating system manages everything, and programmes do specific jobs. Knowing these basics helps us understand how technology works.
Understanding What a Basic Computer System Is
Computer architecture is the blueprint for all digital operations. It sets rules for how hardware and software work together. It defines how processing units, memory, and input-output devices interact.
The way physical parts and instructions work together makes computing smooth. This interaction lets devices do everything from simple math to complex data tasks. The architecture organises these interactions with standard protocols and channels.
Learning about computer systems starts with understanding how parts work together. The central processing unit runs instructions, and memory stores data. Input devices collect information, and output devices show results to users.
These basics help computers work well, no matter the type. From laptops to servers, the same rules apply. This consistency helps developers make programs that work on different hardware.
Key parts of computer architecture include:
- Instruction set architecture defines how software talks to hardware
- Memory hierarchy organises storage for best performance
- Input/output systems handle communication with devices
- Interconnect protocols let components talk to each other
The design of the architecture affects how well a system works. Good design balances power, memory, and speed. This balance is key for smooth operation, whether it’s simple tasks or complex apps.
Today’s computer architectures keep getting better while staying compatible with old systems. New tech fits with the old, saving money on software and hardware. This way of improving systems is common around the world.
Central Processing Unit (CPU): The Core Processor
The central processing unit (CPU) is at the heart of every computer. It’s the main workhorse that makes everything work. It makes decisions and performs tasks every second to keep your computer running well.
Role of the CPU in a Computer System
The CPU is like the computer’s brain. It understands and carries out instructions from both hardware and software. When you use a program or device, the CPU makes sure it works right.
This part of the computer manages data flow. It makes sure information gets to where it needs to go on time. The CPU turns your commands into actions the computer can do.
Key Functions of the CPU
The CPU does many important things for modern computing. It does math, makes logical decisions, and moves data around.
Modern CPUs can do billions of instructions per second. They are measured in gigahertz (GHz). Faster speeds mean computers can work faster, but other things like core count matter too.
Instruction Execution and Processing
The CPU has a cycle for handling instructions: fetch-decode-execute. It gets instructions from memory, then figures out what to do. Then, it does the task using the right parts.
This cycle happens very fast. It lets computers do complex tasks easily. Keeping the CPU cool is important because it gets hot when it works fast.
Control and Coordination of Operations
The CPU does more than just math. It makes sure everything in the system works together. It handles memory, input/output, and makes sure hardware works well.
The CPU decides what tasks to do first and where to use resources. This makes sure important tasks get done quickly. It also lets background tasks keep running smoothly.
Modern CPUs can do many things at once. This makes computers fast and responsive, which is what we expect today.
Random Access Memory (RAM): Temporary Storage for Efficiency
The CPU is like the brain of your computer. RAM is like its immediate workspace. It provides temporary storage for active programs and data processing. Without enough RAM, even the most powerful processor can’t work smoothly.
Purpose and Importance of RAM
RAM is your computer’s short-term memory. It stores information that active programs need quickly. Unlike permanent storage, RAM offers fast data retrieval, key for real-time operations.
The main RAM purpose is to hold data the CPU needs right away. This includes operating system files, application data, and documents you’re working on. When you open a program, it loads into RAM, not your hard drive.
This approach makes processing faster. The computer can access data from RAM quicker than from traditional storage. This efficient memory function keeps your system fast during multitasking.
How RAM Enhances System Performance
RAM capacity affects how well your computer handles tasks at once. More RAM means more programs and files are ready without slowing down. This is key for tasks like video editing or playing games.
When RAM is full, the computer uses the hard drive as virtual memory. This slows things down a lot. You might see your system slow, freeze, or respond slowly.
RAM works with other parts to keep your computer running well. Enough RAM lets your CPU work without waiting for data. For more on how memory works, check out this guide on computer memory functionality.
| RAM Capacity | Recommended Use | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 4GB | Basic computing, web browsing | Minimum for modern systems |
| 8GB | Office applications, moderate multitasking | Comfortable for most users |
| 16GB | Gaming, content creation, heavy multitasking | Excellent performance |
| 32GB+ | Professional workstations, servers | Maximum efficiency |
Choosing the right RAM depends on your needs. Regular users might get by with 8GB. But power users often need 16GB or more. The goal is to match RAM to your typical workload for the best performance.
Remember, RAM is volatile memory that clears when you turn off your computer. This makes it perfect for temporary storage needs. With enough RAM and the right storage, you get a balanced computing experience that’s both fast and reliable.
Storage Solutions: Hard Disk Drives and Solid State Drives
Temporary memory handles tasks right away, but permanent storage keeps your data safe even when the computer is off. These parts are key for data retention. They keep your operating system, apps, and files safe for many power cycles.
Hard Disk Drives for Long-Term Storage
Hard Disk Drives use spinning magnetic platters for computer storage. Mechanical arms read and write data on these disks, like a record player.
HDDs have lots of storage and are cheaper than SSDs. They’ve been around for a long time. They’re great for big files, media, and backups.
Solid State Drives for Speed and Reliability
Solid State Drives use flash memory chips without moving parts. This means no seek times like with HDDs.
SSDs are much faster and can handle shocks better. They’re quiet and reliable, but cost more per gigabyte than HDDs.
| Feature | Hard Disk Drive (HDD) | Solid State Drive (SSD) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Technology | Spinning magnetic platters | Flash memory chips |
| Average Speed | 100-150 MB/s | 500-3500 MB/s |
| Durability | Vulnerable to physical shock | Highly shock-resistant |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost per GB | Higher cost per GB |
| Ideal Use Case | Mass storage, archives | OS installation, frequent access files |
Choosing between HDD vs SSD depends on your budget and needs. Many use SSDs for the OS and apps. HDDs are for extra storage.
Motherboard: The Foundation of Connectivity
The motherboard is at the heart of every computer. It acts as the main circuit board, connecting all parts. This board is key for smooth communication between components.
The motherboard has many connectors and slots. Each one has a special job in the system. Knowing about these helps us see how computers work well.
Components Integrated on the Motherboard
Today’s motherboards have many parts that are essential for computers. The CPU socket is very important. It fits different processors.
RAM slots are where you put memory. Most boards can handle two or four channels for better performance. You’ll also find SATA ports for hard drives and M.2 slots for fast SSDs.
Expansion slots let you add special hardware:
- PCIe x16 slots for graphics cards
- PCIe x1 slots for sound cards and network adapters
- M.2 slots for Wi-Fi cards and storage expansion
Some motherboards come with built-in features like audio and Ethernet. The BIOS/UEFI chip helps start up the computer.
Functions of the Motherboard in System Integration
The motherboard is great at connecting all parts of the system. It makes sure data moves well between components.
It also handles power to all parts. This keeps the computer stable, even when it’s working hard.
Desktop and laptop motherboards are different. Desktops have more room for upgrades, while laptops are more compact.
Choosing between a desktop and laptop motherboard depends on what you need. Desktops are better for upgrading, but laptops are more portable.
Knowing about motherboards helps you choose the right one. It’s important for making your computer work well and for upgrading later.
Power Supply Unit (PSU): Delivering Stable Energy
While processors and memory get most of the attention, no computer works without a proper energy supply. The power supply unit is key, linking your wall outlet to all parts inside. It makes sure each gets the right voltage.
Role of the PSU in Computer Operation
The power supply unit does vital work. It changes alternating current from your wall socket into direct current for computer parts. It does this at different voltages to meet each part’s needs.
Modern PSUs send power through special cables to different parts of the system. The motherboard gets main power through big connectors. Other cables go to storage drives, graphics cards, and more. This setup makes sure each part gets exactly what it needs.
Importance of a Reliable Power Supply
System stability relies on steady computer power delivery. Fluctuations in voltage can lead to crashes, data loss, or damage to parts. A good PSU keeps voltages steady, even when the power grid changes.
PSUs also have protection features. Good ones guard against power surges, short circuits, and overloads. These features help prevent damage to expensive parts during power issues.
Efficiency ratings show how well a PSU uses electricity. A higher rating means less energy wasted as heat and lower bills. Look for 80 Plus certification when picking a power supply.
Choosing a reliable power supply means stable electricity for all parts. This base helps avoid many problems and keeps your computer running smoothly for years.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Handling Visual Output
The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is key for computer graphics. It handles all visual data processing, turning digital info into what we see on screens. The GPU’s role has grown from just showing images to handling complex graphics in many apps.
Function of the GPU in Rendering Graphics
The GPU is the main engine for visual work in computers. It uses parallel processing to handle complex graphics tasks efficiently. This includes making images, animations, and effects for monitors.
Modern GPUs do many important tasks in graphics processing:
- Vertex processing for 3D object positioning
- Pixel shading for colour and texture application
- Rasterisation for converting vectors into pixels
- Anti-aliasing for smoothing jagged edges
These tasks happen millions of times a second for smooth visuals. The fastest GPUs are best for gaming and professional visual work.
Integrated vs Discrete GPUs
There are two main GPU types in computers. Knowing the differences helps users choose the right one for their needs.
Integrated GPUs are built into the motherboard or processor. They use system memory with the CPU. This is good for saving money and power for simple tasks.
Discrete GPUs are separate cards with their own memory and cooling. They offer superior performance for heavy graphics work. They’re great for gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
| Feature | Integrated GPU | Discrete GPU |
|---|---|---|
| Performance Level | Basic to moderate | High to exceptional |
| Memory Usage | Shares system RAM | Dedicated VRAM |
| Power Consumption | Lower energy usage | Higher power demands |
| Primary Use Cases | Office applications, web browsing | Gaming, professional design |
| Cost Consideration | Included with processor/motherboard | Additional purchase required |
Most computers have integrated graphics for everyday tasks. But, for advanced graphics, you need a discrete card.
Choosing between integrated and discrete GPUs affects your system’s visuals and performance. Think about your graphics needs before picking a GPU.
Input and Output Devices: Enabling User Interaction
Computer systems need good ways for users and machines to talk to each other. Input and output devices are key to this, turning what we want into digital commands and showing us the results.
Common Input Devices like Keyboard and Mouse
Keyboards and mice are the basics in computing. They let us type, click, and move around digital spaces with ease.
Today’s keyboards have many types of keys. They can connect with wires or wirelessly. Mice use light to track movement, with extra buttons and scroll wheels for more control.
There are many other input devices too:
- Scanners turn paper into digital files
- Digital cameras capture images and video
- Microphones record sound for talking and recording
- Touchscreens are both input and output in one
Common Output Devices such as Monitor and Printer
Output devices show us what the computer has done. Monitors are the main way we see things, like pictures and text. They use new tech like LCD and OLED for clear images.
Printers make hard copies of what’s on the screen. Inkjet is good for photos, while laser is better for lots of text. You can connect them with wires or wirelessly.
Other output devices help too:
- Speakers and headphones play sound
- Projectors show things on big screens
- Braille readers help the visually impaired
These devices use standard connections like USB and HDMI. New tech like gesture control and voice recognition are making it easier for us to talk to computers.
Interaction of Core Components in System Operation
Every computer system has a network of parts working together. This component interaction is key for all computing tasks. The motherboard acts as the brain, connecting all parts.
When you use devices like keyboards, it starts a chain of events. The data goes to the CPU, which then talks to other parts. This is how computers work.
The motherboard is vital in this process. It connects and carries data between parts. The CPU, RAM, storage, and GPU all use the motherboard to work together.
Data moves quickly and follows set paths. The CPU gets instructions, processes them, and saves the results. This happens fast, in nanoseconds.
Components work together in sync. The CPU’s speed sets the pace, and others adjust. This ensures data is used when needed.
Each part of the system helps the others. RAM gives the CPU quick access to data. Storage keeps data safe. The GPU handles graphics, letting the CPU focus on other tasks.
| Component | Primary Function | Interaction Partners | Data Exchange Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Central Processing | RAM, Motherboard, Storage | Instruction/Data Transfer |
| RAM | Temporary Data Storage | CPU, Motherboard, Storage | High-Speed Data Access |
| Storage Drives | Permanent Data Storage | CPU, RAM, Motherboard | Data Retrieval/Storage |
| GPU | Graphics Processing | CPU, RAM, Motherboard | Visual Data Processing |
| Motherboard | Component Connectivity | All Components | Power & Data Pathways |
This component interaction makes computing smooth. From starting up to running apps, it all works together. The system’s performance depends on how well these parts work together.
Knowing how this works shows how amazing computers are. Each part has its role, making the system work better. Upgrading parts can boost performance.
The beauty of this computer workflow is that users don’t see it. Yet, they enjoy fast and smooth computing. This is the power of integrated computing – making complex simple.
Conclusion
A basic computer system is a complex mix of hardware parts working together. Each part has its role in making the system work. The CPU handles instructions, RAM stores data temporarily, and storage devices keep it safe for a long time.
Computers are incredibly fast, doing millions of calculations every second. They are also very accurate, following instructions without making mistakes. This shows their ability to handle complex tasks with ease.
This summary highlights how these parts make computers reliable. From the motherboard to the PSU, each part is vital. The mix of hardware and software gives us the computing power we use every day.
These basic principles apply to all computers. Knowing how they work helps us understand technology better. It shows us the importance of each part in making computers work.
FAQ
What are the core components of a basic computer system?
A basic computer system has key parts. These include the CPU, RAM, and storage like HDD or SSD. The motherboard, PSU, GPU, and input/output devices like keyboards and monitors are also important. They work together to process and store data well.
How does the CPU function as the brain of the computer?
The CPU is like the brain. It fetches, decodes, and executes instructions. It handles data, does calculations, and manages other parts. This ensures the system works smoothly.
Why is RAM important for computer performance?
RAM is key for fast performance. It stores data for running programs. Without enough RAM, computers can be slow, even when doing simple tasks.
What is the difference between an HDD and an SSD?
HDDs store data on magnetic platters. They are cheaper but slower. SSDs use flash memory and are faster but more expensive.
What role does the motherboard play in a computer system?
The motherboard connects all parts. It lets them talk to each other and share power. It’s vital for the system to work right.
How does the Power Supply Unit affect computer stability?
The PSU changes wall current to what components need. A good PSU keeps energy stable. It protects parts and is key for system health.
What is the function of the GPU in a computer?
The GPU makes images and videos for the screen. It’s great for games and design. It makes visuals better.
How do input and output devices facilitate user interaction?
Input devices like keyboards send commands. Output devices like monitors show what’s processed. They help users and computers talk to each other.
How do all core components interact during system operation?
Components work together through the motherboard. For example, input turns into data for the CPU. The GPU then makes it visible. This teamwork makes the system work well.
Can I upgrade components in a laptop as easily as in a desktop?
Laptop upgrades are harder than desktops. Laptops are smaller and parts are often fixed. Desktops are easier to upgrade.
What should I consider when choosing between an integrated and discrete GPU?
Integrated GPUs are good for basic tasks. Discrete GPUs are better for games and heavy graphics. Choose based on what you need and can afford.
How does processor speed, measured in GHz, impact computer performance?
Processor speed is in GHz. Higher means faster. But, other things like cores and architecture matter too. Speed alone isn’t everything.